A New AI Framework Is Turning Everyday Online Photos Into Realistic 3D Scenes
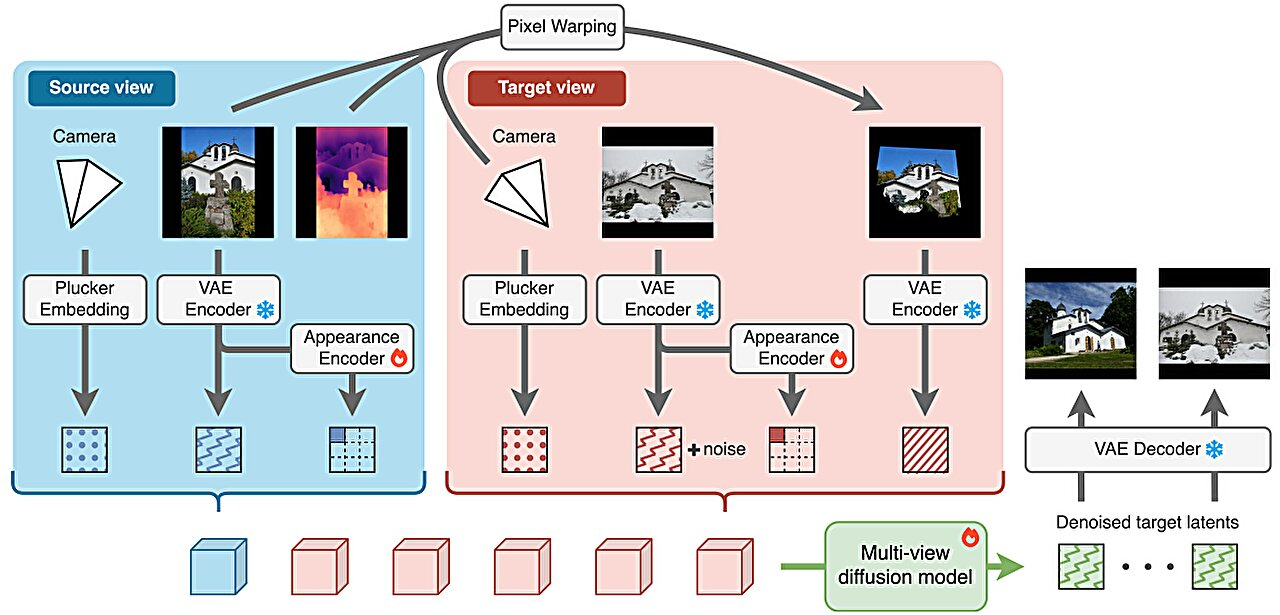
Researchers are making a major leap in how computers understand and recreate the world in three dimensions, using nothing more than the kinds of photos people casually upload online every day. A new framework called WildCAT3D is changing what’s possible in 3D scene generation by learning directly from messy, real-world images instead of relying on carefully curated datasets.
The work focuses on a long-standing challenge in computer vision: how to generate realistic 3D environments from a single photo when that photo comes from uncontrolled conditions like changing weather, lighting, seasons, and camera angles. This breakthrough opens new doors for industries such as gaming, virtual tourism, cultural preservation, and immersive digital mapping.
What WildCAT3D Is and Why It Matters
WildCAT3D is a new novel view synthesis (NVS) framework developed by a team of researchers including Hadar Averbuch-Elor, an assistant professor at Cornell Tech and a faculty member at the Cornell Ann S. Bowers College of Computing and Information Science. Novel view synthesis is a technique that allows a system to generate new, realistic viewpoints of a scene based on one or more existing images.
Traditionally, NVS systems work best only when trained on small, highly controlled datasets. These datasets are usually captured under consistent lighting, stable weather, and carefully planned camera positions. While that makes training easier, it also means the models struggle when faced with real-world photos taken by everyday users.
WildCAT3D takes a very different approach. Instead of avoiding imperfect data, it embraces the chaos of the internet, learning directly from large collections of freely available photos such as tourist snapshots, images taken in different seasons, scenes partially blocked by people or objects, and photos shot under wildly different lighting conditions.
The Core Problem With Existing 3D Models
Most existing 3D image-generation systems fail when confronted with “in-the-wild” data. Photos shared online often vary drastically in appearance, even when they depict the same location. Shadows shift, skies change, rain and snow appear, and temporary objects like cars or crowds come and go.
For current models, these variations are confusing. They often interpret appearance changes as changes in structure, which leads to distorted or inconsistent 3D reconstructions. This limitation has made it difficult to use everyday photos for large-scale 3D modeling projects.
The WildCAT3D team set out to solve this exact problem by asking a simple but powerful question: how can a model learn the stable structure of a scene while ignoring temporary visual changes?
How WildCAT3D Overcomes These Challenges
WildCAT3D introduces an appearance-aware multi-view diffusion model designed specifically to handle inconsistent real-world imagery. Instead of treating every difference between images as equally important, the system learns to separate what stays the same from what changes.
The model focuses on stable elements such as buildings, terrain, and permanent landmarks, while treating variations in lighting, weather, seasonal effects, and transient objects as secondary details. This allows the system to build a consistent internal representation of a place, even when the training images look very different from one another.
By doing this, WildCAT3D can be trained on large-scale internet image collections that were previously unusable for 3D learning. This is a significant shift away from reliance on tightly controlled datasets and toward permissively licensed online data.
From a Single Photo to Multiple Realistic Views
One of the most impressive capabilities of WildCAT3D is its ability to take a single photo and generate multiple realistic views of the same scene. In practical terms, this means a user could upload one image of a location and then explore it from different angles, almost as if they were walking around it.
This capability is especially valuable for applications like virtual tourism, where users want to explore places they may never physically visit. It also has clear benefits for video game development, where realistic environments are essential but expensive to create manually.
In addition, the framework allows researchers and creators to visualize how a scene might appear under different lighting or weather conditions, making it useful for planning, simulation, and design.
Why Diffusion Models Matter Here
WildCAT3D builds on recent advances in diffusion-based generative models, which have become widely known for their success in image generation. Diffusion models work by gradually transforming noise into meaningful structure, allowing them to produce highly realistic outputs.
By adapting diffusion techniques to multi-view 3D learning, the researchers were able to create a system that maintains 3D consistency across generated views. This is a crucial requirement for believable 3D scenes and one of the hardest problems in the field.
The result is a framework that not only produces visually convincing images but also respects the underlying geometry of the scene.
Real-World Applications and Long-Term Impact
The potential applications of WildCAT3D span multiple industries:
- Gaming and virtual reality, where immersive environments are essential
- Virtual tourism, enabling exploration from limited photographic material
- Cultural and historical preservation, especially for landmarks that may be damaged, altered, or difficult to document
- Urban planning and architecture, allowing planners to visualize spaces before construction or restoration
- Digital mapping and simulation, where accurate 3D reconstructions improve realism and usability
By lowering the barrier to high-quality 3D scene creation, WildCAT3D makes it possible for individuals and small teams—not just large studios or research labs—to build realistic digital environments.
A Shift in How 3D AI Models Are Trained
One of the broader implications of this work is its challenge to the current norms of dataset creation. For years, progress in 3D vision has depended on expensive, manually curated datasets. WildCAT3D suggests a future where models can learn directly from the visual data people already share online.
This shift could dramatically accelerate research and development while making 3D technology more accessible and inclusive. It also aligns with a growing trend in AI toward systems that can learn robustly from imperfect, real-world data.
Presentation and Publication Details
The WildCAT3D framework was presented on December 4, 2025, at the Conference and Workshop on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2025), one of the most influential conferences in artificial intelligence and machine learning. The research paper is also available on the arXiv preprint server, making it accessible to researchers worldwide.
The full paper, authored by Morris Alper and colleagues, provides detailed technical insights into the architecture, training process, and evaluation of the system.
Looking Ahead
WildCAT3D represents an important step toward 3D-consistent generative AI that works in real-world conditions. By learning from everyday photos instead of idealized datasets, the framework brings AI-generated 3D environments closer to how people actually capture and experience the world.
As research in this area continues, systems like WildCAT3D could become foundational tools for building the next generation of digital spaces, from entertainment and education to preservation and planning.
Research paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.13030