Researchers Develop G2PDeep, a Powerful Deep Learning Platform Designed to Push Precision Medicine Forward
Researchers from Marshall University and the University of Missouri have jointly developed a new deep learning platform called G2PDeep, a web-based tool built to tackle one of modern biology’s biggest challenges: making sense of massive, complex biological datasets to improve health prediction and personalized treatment. The platform uses advanced artificial intelligence to analyze multiple layers of biological data at once, allowing scientists to make more accurate predictions about disease risk, health outcomes, and phenotypic traits.
The research describing G2PDeep has been published in the peer-reviewed journal Biomolecules, highlighting its scientific validation and growing relevance in the fields of precision medicine, bioinformatics, and computational biology.
At its core, G2PDeep is designed to bridge the long-standing gap between genotype and phenotype—in other words, how genetic and molecular information translates into observable traits, diseases, or responses to treatment. This connection has traditionally been difficult to model because biological systems are influenced by many interacting molecular layers rather than a single data source.
What Makes G2PDeep Different From Existing Tools
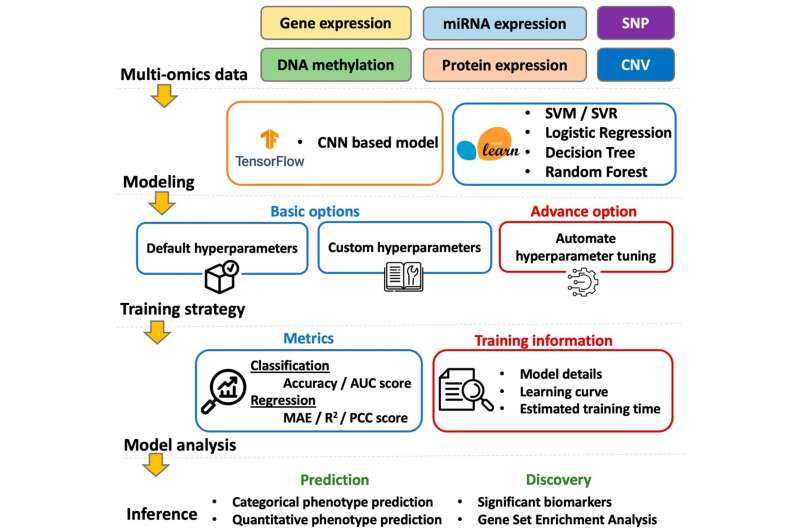
What sets G2PDeep apart is its ability to integrate six major types of molecular data into one unified deep learning framework:
- Gene expression data
- microRNA (miRNA) expression
- Protein expression
- DNA methylation profiles
- Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
- Copy number variations (CNVs)
Each of these data types captures a different aspect of biological activity. Gene expression shows which genes are active, miRNAs regulate gene behavior, proteins execute cellular functions, DNA methylation reflects epigenetic changes, SNPs capture genetic variation, and CNVs reveal structural changes in the genome. By analyzing all six together, G2PDeep provides a more holistic view of biological systems than tools that focus on just one or two data types.
The platform uses deep learning models to combine these datasets and generate highly accurate phenotype predictions. This approach allows researchers to identify omics-based molecular markers that differentiate patient groups, predict disease susceptibility, and reveal how individuals may respond to treatments.
A Web-Based Platform Built for Accessibility
Another major strength of G2PDeep is that it is fully web-based, meaning researchers and clinicians do not need extensive programming expertise or powerful local computing resources to use it. Users can upload datasets, configure prediction models, and analyze results directly through a browser-based interface.
This accessibility is important because many advanced AI tools remain out of reach for biomedical researchers who lack deep technical backgrounds. G2PDeep lowers that barrier by turning sophisticated deep learning methods into a practical, user-friendly platform that can be widely adopted across research institutions.
Advancing Precision Medicine and Patient Care
One of the most promising applications of G2PDeep lies in precision medicine, where treatments and prevention strategies are tailored to individual patients rather than applied uniformly. By integrating diverse molecular datasets, the platform helps researchers uncover the biological mechanisms that drive disease risk and treatment response.
The research team highlights that G2PDeep can support studies across a wide range of health conditions, including cancer, addiction, aging, obesity, kidney disease, and other chronic illnesses. These diseases are especially relevant to populations in Appalachia and the Midwest, regions that experience significant health disparities and elevated rates of certain conditions.
By enabling better risk assessment and more precise patient stratification, G2PDeep has the potential to guide clinicians toward more informed decision-making and help researchers design interventions that are better matched to individual biology.
Beyond Medicine: Applications in Agriculture and Biotechnology
While G2PDeep was developed with human health in mind, its design intentionally supports all organisms, not just humans. This makes it valuable for agribiotech and plant science research as well.
When applied to agricultural datasets, the platform can help plant breeders build predictive models for important phenotypic traits such as yield, stress tolerance, disease resistance, and resilience to environmental change. By identifying molecular markers associated with these traits, researchers can make data-driven improvements in crop performance, which is increasingly important in the face of climate variability and global food demands.
This cross-disciplinary flexibility reflects a broader trend in bioinformatics: tools built for medicine often have powerful applications in agriculture, ecology, and evolutionary biology when designed with adaptability in mind.
The Collaborative Effort Behind the Platform
The development of G2PDeep represents a long-term academic collaboration between Marshall University and the University of Missouri. Researchers involved in the project emphasize that the goal was not simply to develop a new algorithm, but to create a robust platform that the broader research community could actually use.
The team focused on translating cutting-edge AI techniques into a tool that balances technical sophistication with real-world usability. This approach reflects a growing recognition in computational science that impactful innovation depends as much on accessibility as it does on raw performance.
Understanding Multi-Omics and Why It Matters
To fully appreciate G2PDeep’s significance, it helps to understand the concept of multi-omics integration. Traditional studies often examine one data type at a time—such as genomics or transcriptomics—because integrating multiple datasets is computationally challenging. However, diseases rarely arise from a single molecular factor.
Multi-omics approaches capture interactions across biological layers, revealing insights that would otherwise remain hidden. Deep learning models are especially well-suited for this task because they can detect non-linear relationships and complex patterns that simpler statistical methods miss.
G2PDeep leverages this strength of deep learning to move beyond correlation and toward predictive understanding, which is essential for both clinical and research applications.
A Step Toward More Predictive Biology
The release of G2PDeep reflects a broader shift in biomedical research toward predictive, data-driven biology. Instead of simply describing biological systems, platforms like this aim to anticipate outcomes, identify risk earlier, and guide interventions more precisely.
As biological datasets continue to grow in size and complexity, tools that can integrate, analyze, and interpret them effectively will become increasingly important. G2PDeep represents a meaningful step in that direction, combining advanced AI with practical design to support research across medicine and agriculture.
More details about the study can be found in the original research paper:
https://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/15/12/1673